Abstract Control Number: 6689 | AACR 2025
Streck Research and Development, La Vista, NE
Evaluating the influence of collection tubes and extraction kits on miRNA recovery in cancer biomarker research
Eunju Seong, Ph.D., Nicholas M George, Ph.D., Jordan LaRue, Jing Li, Ph.D., and Lisa Bartron, MB(ASCP).
INTRODUCTION
Cell-free RNAs, especially microRNAs (miRNAs), are emerging as valuable biomarkers in cancer research and other diseases. These small, non-coding RNA molecules circulate in the bloodstream, offering insights into the physiological and pathological states of various organs and tumors. However, the stability of miRNAs in blood samples can be significantly affected by the type of blood collection tube used and the handling and processing of blood samples. While the extraction of miRNAs from plasma or serum is critical for their analysis, the choice of extraction kit can significantly influence the yield and quality of the isolated RNA. Here, we compare three plasma miRNA extraction kits paired with various blood collection tubes – EDTA, ACD-A, citrate, Nucleic Acid BCT™, and Protein Plus BCT™. Our data show that the recovery of miRNA and mRNA from plasma samples is significantly influenced by the combination of RNA extraction kit and blood collection tube. Further, this work demonstrates that Nucleic Acid BCT and Protein Plus BCT better maintain draw-time plasma miRNA levels compared to conventional anticoagulants.
Nucleic Acid BCT and Protein Plus BCT are for Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic procedures. Nucleic Acid BCT and Protein Plus BCT should only be used for research or the development of new assays.
METHODS
Blood from self-declared healthy donors was collected into EDTA, ACD-A, citrate, Nucleic Acid BCT, and Protein Plus BCT and immediately mixed end-over-end 10 times. Following draw or after 1, 3, or 5 days of ambient temperature storage, tubes were remixed end-over-end 10 times, then samples were processed to plasma using a double-spin protocol (1800 xg for 15 min, 2800 xg for 15 min).
For the RNA extraction kit comparison study, plasma was pooled from all donors (n=5), aliquoted, and frozen at -80 ˚C until use. RNA extractions were executed per the manufacturer’s protocols, where plasma input volume per RNA extraction kit was as follows:
- 500 μL – Plasma/Serum Circulating and Exosomal RNA Purification Kit (Slurry Format; Norgen, 51000)
- 200 or 500 μL – Maxwell® RSC miRNA Plasma and Serum Kit (Promega Corporation, AS1680)
- 200 μL – QIAGEN miRNeasy Serum/Plasma Kit (QIAGEN, 217184)
For RNA spike-in experiments, 0.1 μL UniSP2/4/5 (QIAGEN, 339290) per 100 μL plasma was added to the lysis reagent.
For the miRNA stability study, RNA was extracted from 200 μL of individual plasma samples using the Promega kit.
For each tube and timepoint, extraction was performed in triplicate for the RNA extraction kit study and in singlicate for the miRNA stability study, and PCR was run in duplicate. All PCR assay outcomes were plotted without averaging. miRNAs were quantified by qRT-PCR using the miRCURY® LNA® RT and SYBR™ Green PCR Kits and miRCURY LNA miRNA PCR Assays (QIAGEN). The plots display Ct (Cycle threshold) values adjusted to equalize the differences in the plasma input and elution volumes of RNA extraction.
Maxwell Systems and the Maxwell RSC miRNA Plasma and Serum Kit are for Research Use Only.
Not for use in diagnostic procedures.
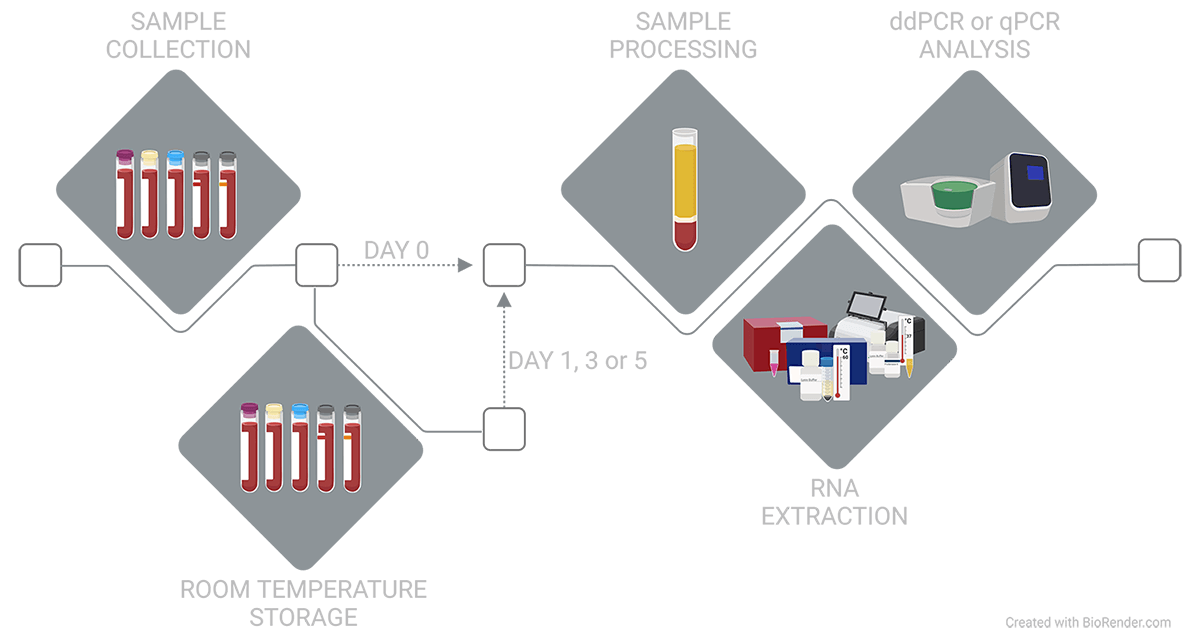
Figure 1. Blood from self-declared healthy donors was collected into EDTA, ACD-A, citrate, Nucleic Acid BCT, or Protein Plus BCT. At draw or after 1, 3, or 5 days at ambient temperature, plasma was isolated, then miRNA or mRNA was extracted and analyzed.
RESULTS
RNA extraction kit choice affects plasma miRNA and mRNA recovery
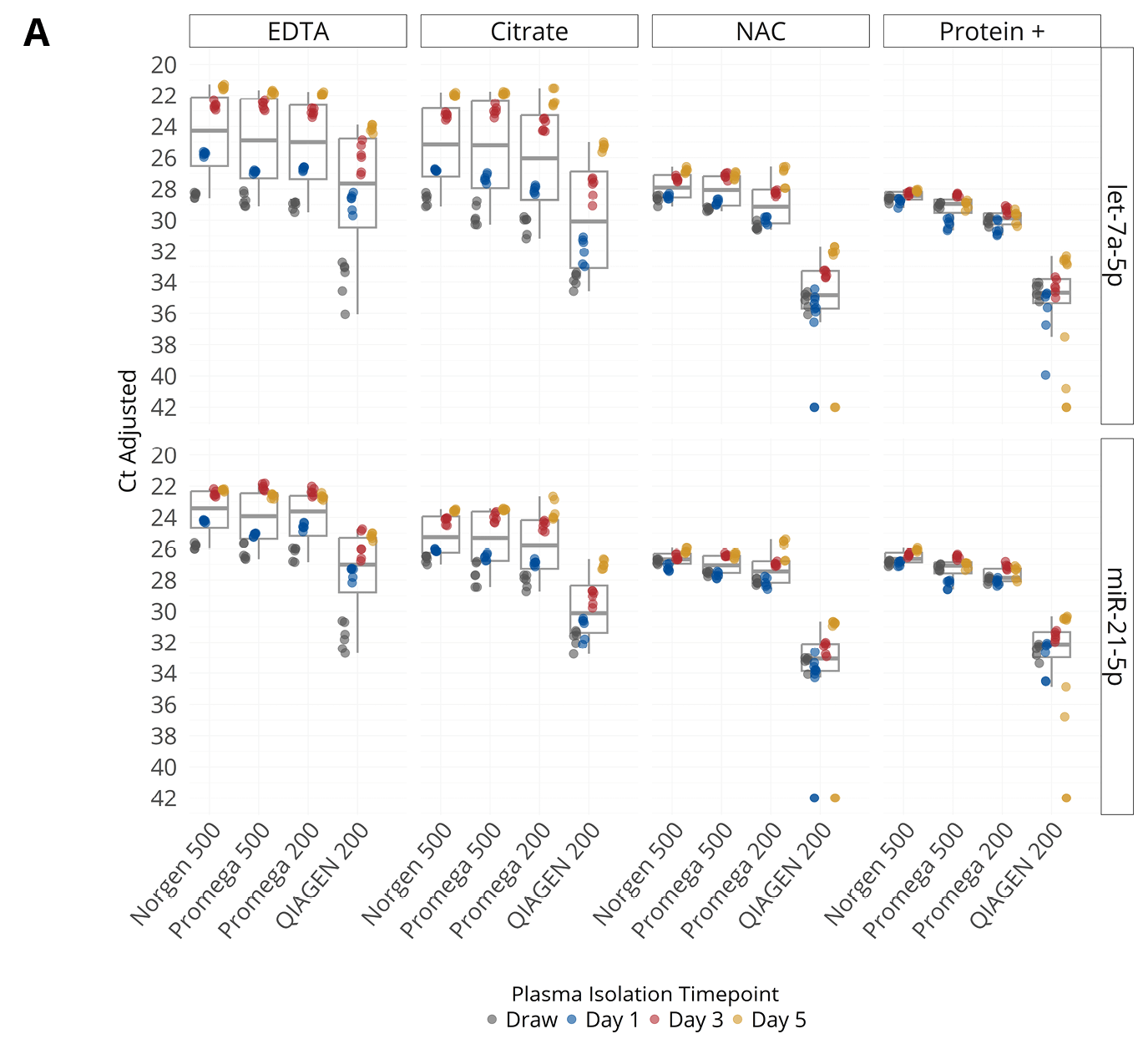
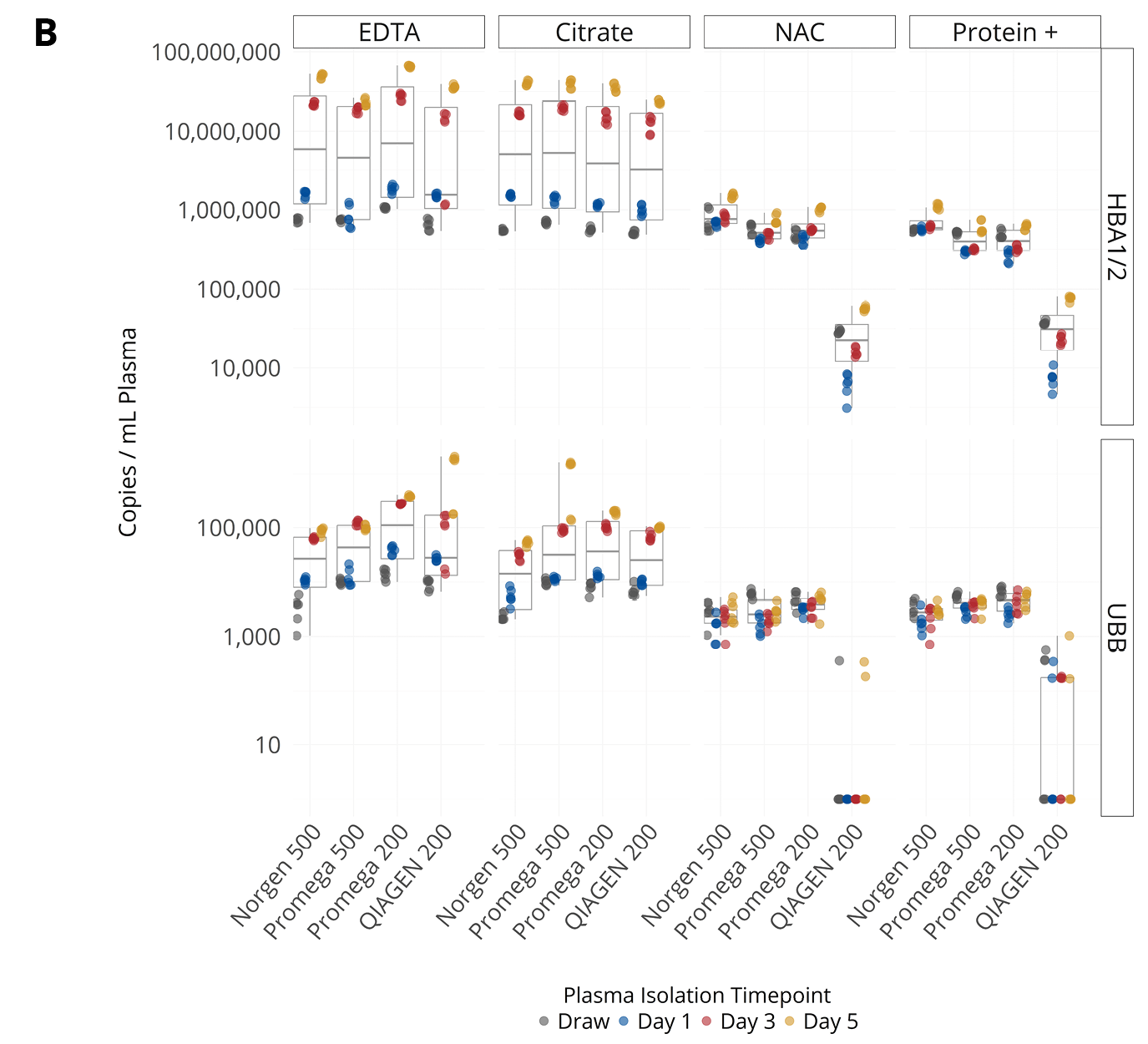
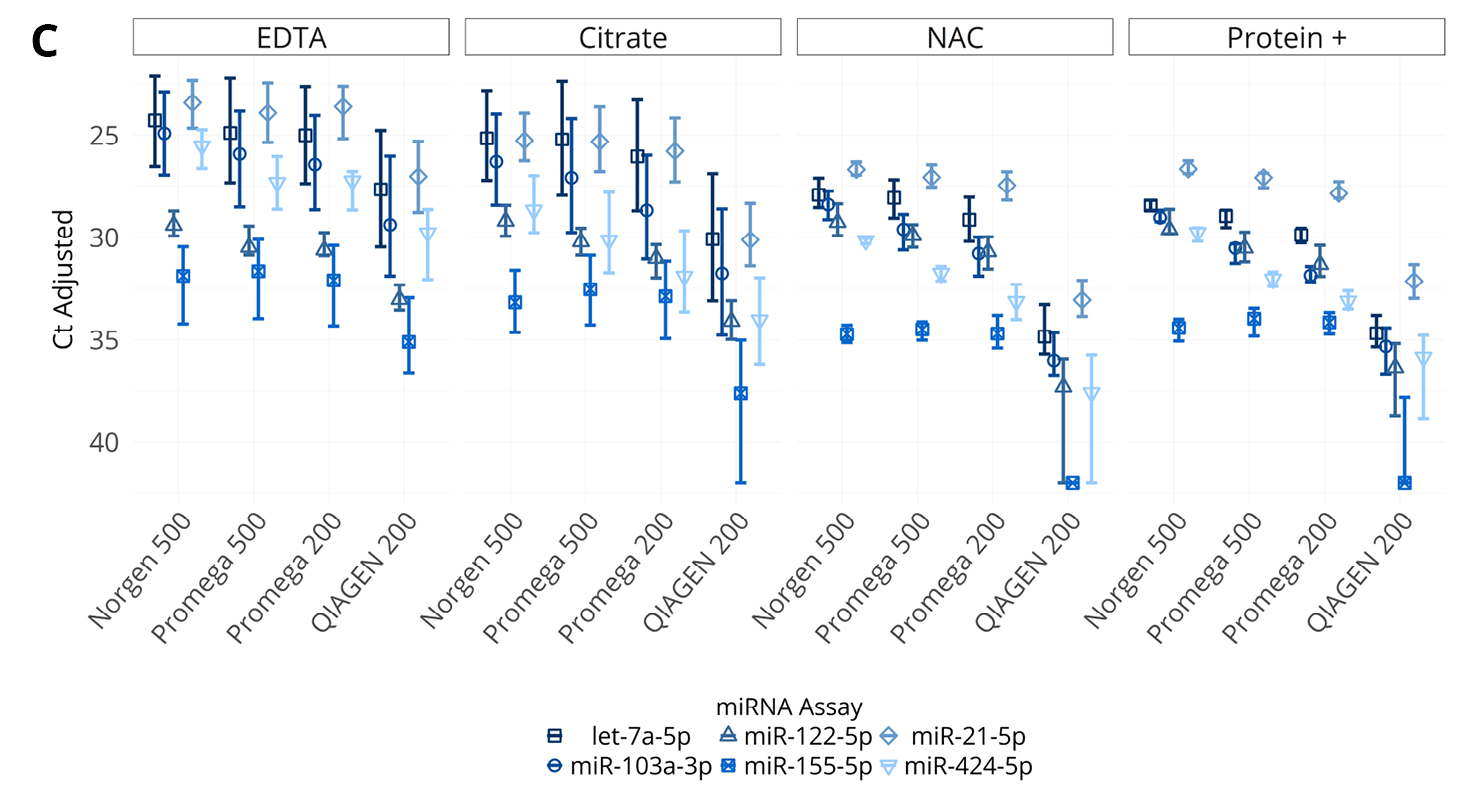

Figure 2. (A, B) Concentration of endogenous miRNA (A) or mRNA (B) in plasma isolated from samples collected into EDTA, citrate, Nucleic Acid BCT (NAC), and Protein Plus BCT (Protein+). miRNA concentrations are shown as Ct values on the Y-axis in reverse scale and mRNA concentrations are shown as copies / mL plasma (pooled plasma from 5 donors). (C, D) Abundance (Ct) of various endogenous miRNA (C) and spiked-in RNA (D) in plasma isolated from samples collected into EDTA, citrate, NAC and Protein+. The bar represents interquartile range of miRNA or RNA Spike-In concentration in samples from draw to day 5. The x-axis labels correspond to RNA extraction kit choices and input volumes (in μL).
Draw-time plasma miRNA concentrations are maintained in samples collected into Nucleic Acid BCT and Protein Plus BCT

Figure 3. Concentration of various miRNA extracted from plasma isolated from samples collected into EDTA, ACD-A, Nucleic Acid BCT (NAC), and Protein Plus BCT (Protein+) using the Maxwell RSC miRNA, Plasma and Serum Kit (Promega, 200 μL sample volume). miRNA concentrations are shown as Ct values on the Y-axis in reverse scale. The x-axis is stratified based on donor (n=6, labeled A-F).
CONCLUSIONS
These data underscore the immense importance of selecting appropriate blood collection tubes and extraction kits to optimize miRNA recovery from plasma samples. Careful consideration of these factors is essential for obtaining reliable results in clinical studies involving circulating miRNAs. When paired with the automated miRNA extraction kit from Promega Corporation (Maxwell RSC miRNA Plasma and Serum Kit), Nucleic Acid BCT and Protein Plus BCT provide researchers flexibility in sample processing and shipping protocols without concern for ex vivo changes to the sample composition or resultant suboptimal analyte recovery.


